Laparoscopic Appendectomy describes the removal of inflammation appendix through a small incision made in the abdomen. The appendix is a small organ located on the lower side of the abdominal cavity. It aids in the prevention of bacterial infection in the body.Appendicitis can be caused when the appendix gets blocked partially or completely causing inflammation of the organ and formation of pus. The blockage of the appendix can be with the production of thick mucus or stool enters the organ from the intestine. When the organ gets blocked the bacteria residing within will multiple. In response to the infection, the organ swells.
Symptoms of Appendicitis Include:
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Loss of Appetite
- Nausea and Vomiting
- High Fever
- Constipation.
- Diagnosing Appendicitis
Patient’s Historical Records are checked for the following factors:
- The Rise in White Blood Cell Count
- Urinalysis
- Abdominal X-ray
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
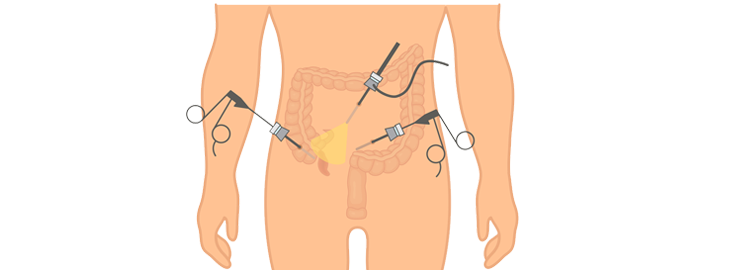
Treatment for Appendectomy
Laparoscopic appendectomy is the common treatment available for appendicitis. The surgery procedure includes removing the appendix through a small incision made in the lower abdomen and the activity are monitored via camera.
Laparoscopic appendectomy surgery is undergone by patients whose infection is less spread in the body. The surgery includes making a small cut in the lower abdomen and a lean and narrow tube (cannula) is entered into the abdomen. A laparoscope (an instrument that has a telescope linked to a video camera) is then inserted through the tube so that the surgeon can view the internal organ as enlarged images and perform tasks by entering more tubes into the abdomen. The infected appendix is cut from the colon and the hole is sewed through the tube. The pus from the infected appendix is also removed via cannula. The incisions are then closed.
In some cases, an appendectomy can be followed by a medical condition termed as Adhesiolysis. This is a common difficulty that is accompanied after having abdominal surgeries. Unlike open Surgeries, Laparoscopic Surgeries have a low probability for Adhesions.
Adhesions are formed as part of the normal healing process. It forms a band of tissues formed between the organs to protect them. Some are indicated by pain and restriction in bowel movement. In such cases, adhesions can bind together tissues of organs causing improper functioning of organs. They are visible as thin or thick sheets of fibrous tissue bands of adhesions. In most cases, surgeons suggest adhesiolysis were scar tissues are removed along laparoscopic appendectomy.
Patients who have to undergo Adhesiolysis Treatment are Assessed when
- Pain is not Reduced
- Continuous Vomiting
- Chilled Body
- Constant Coughs
- Redness and Pus Formation in Area around Incision
- Loss of Appetite.
After Laparoscopic appendectomy surgery followed adhesiolysis or devoid of adhesiolysis, in either case, patient covers pain and has fast recovery from surgery. Patients are told to do small activities to prevent any chances of blood clots or soreness. Nevertheless, care should be taken to not develop any infection by following proper care and medications.
