Synopsis
Laparoscopy, often referred to as “keyhole surgery,” has revolutionized modern surgical practices by offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgery. This advanced technique is used to diagnose and treat a variety of medical conditions with smaller incisions, faster recovery times, and fewer complications. In this blog, we will explore what laparoscopy is, how it works, and how it compares to traditional surgery. We will also discuss the common conditions that can be treated using this technique, offering a comprehensive guide to its growing importance in healthcare.
What is Laparoscopy?
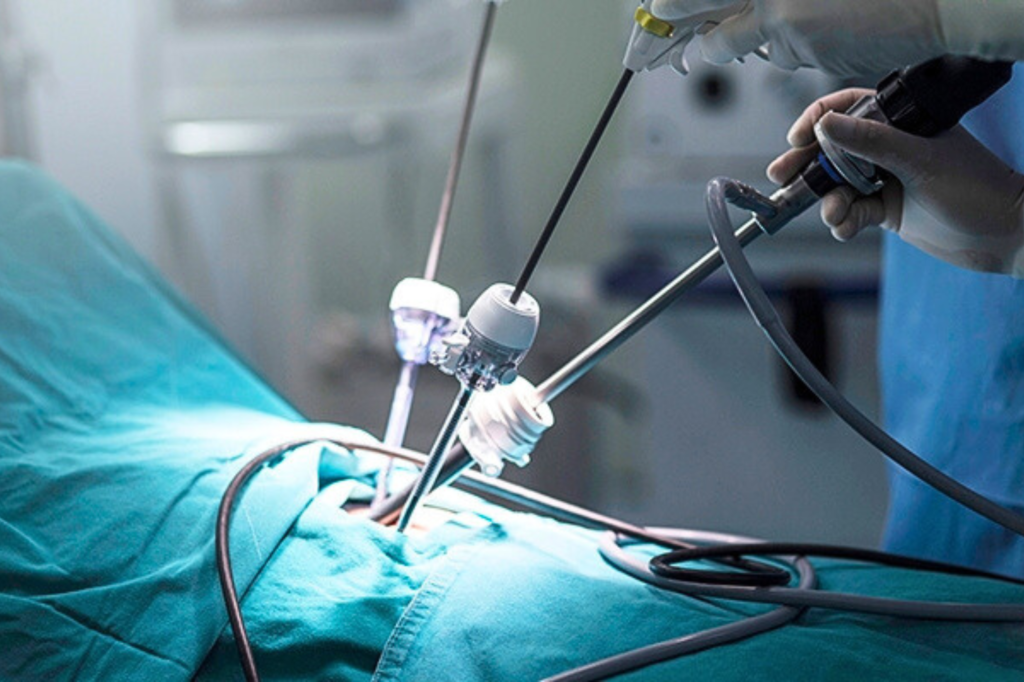
Laparoscopy is a type of minimally invasive surgery that involves making small incisions, usually less than an inch in size, through which a surgeon inserts a laparoscope—a long, thin tube with a camera and light. This tool allows the surgeon to view the internal organs on a monitor in real-time, providing a clear and detailed view without the need for large, open incisions. Through the laparoscope, surgeons can perform diagnostic procedures or use other specialized instruments to treat a variety of conditions with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
Laparoscopic surgery is used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It enables surgeons to identify and treat medical conditions such as gallstones, hernias, and reproductive health issues with greater precision, making it an ideal option for patients seeking a quicker, less invasive treatment.
How Does it Differ from Traditional Surgery?
The primary difference between laparoscopy and traditional open surgery lies in the size and number of incisions required. Traditional surgery often requires a large incision to access the affected area, which can lead to significant trauma to the body, longer recovery times, and more extensive scarring. In contrast, laparoscopy requires only small incisions, typically between 0.5 to 1 cm, which results in minimal tissue damage.
Here are some key advantages of laparoscopic surgery over traditional open surgery:
- Smaller Incisions: Traditional surgery requires large cuts to access internal organs, while laparoscopy only requires small incisions. This minimizes the risk of infection and reduces scarring, leaving patients with less noticeable marks after the procedure.
- Quicker Recovery: One of the most significant benefits of laparoscopic surgery is the speed of recovery. Because the incisions are smaller and less invasive, patients experience less pain and can usually return to their normal daily activities much faster than those undergoing traditional surgery.
- Less Pain: Laparoscopic surgery typically causes less pain because it does not involve large cuts through muscle or tissue. As a result, patients generally require less pain medication and have a more comfortable postoperative experience.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Since laparoscopy involves smaller incisions, there is a reduced risk of complications such as infection or excessive bleeding. The precision of the procedure also allows for better control and minimizes the possibility of damage to surrounding organs.
- Better Visualization: The laparoscope provides high-definition visuals of the internal organs, which helps the surgeon navigate with greater accuracy. This enhanced view is particularly beneficial for delicate procedures, as it allows for better decision-making during surgery.
Common Conditions Treated
Laparoscopy is used to treat a wide range of conditions, especially those involving the abdomen and pelvis. Below are some of the most common conditions for which laparoscopy is often recommended:
- Gallbladder Disease (Cholecystectomy): One of the most common uses of laparoscopy is for gallbladder removal, or cholecystectomy, particularly when gallstones cause pain or inflammation. The laparoscopic approach offers numerous advantages, including quicker recovery times and smaller incisions. Most patients are able to return home on the same day or the following day after the procedure.
- Hernia Repair: Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive technique used to treat hernias, including inguinal (groin) and ventral hernias. During this procedure, the surgeon makes small incisions and uses specialized tools to push the hernia back into place and secure it with mesh. This method causes less pain, reduces the risk of recurrence, and allows for a faster recovery compared to traditional open hernia repair.
- Endometriosis: Laparoscopy is a vital tool in diagnosing and treating endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. Using laparoscopy, surgeons can remove the endometrial tissue from affected areas, which helps alleviate symptoms like chronic pelvic pain and infertility.
- Ovarian Cysts and Uterine Fibroids: Women with ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids can benefit from laparoscopic surgery to remove these growths with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. This procedure is less painful and allows for a quicker recovery compared to traditional surgery.
- Bariatric Surgery: Laparoscopic techniques are also used in bariatric (weight-loss) surgeries, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy. These procedures are performed through small incisions and have become the standard in bariatric surgery due to their reduced complication rates, quicker recovery, and smaller scars.
- Appendicitis: In cases of appendicitis, laparoscopic appendectomy is a less invasive alternative to open surgery. The procedure involves removing the appendix through small incisions, which results in less pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
- Reproductive Health Issues: Laparoscopy is often used in gynecological procedures, such as tubal ligation, infertility treatments, and fibroid removal. It is particularly useful for diagnosing issues with the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and uterus, providing a clearer view and reducing the risk of complications.
The Future of Laparoscopy
As technology continues to advance, laparoscopy is likely to become even more precise and effective. With the integration of robotic assistance, surgeons can perform procedures with even greater accuracy, improving patient outcomes and reducing recovery times even further. Minimally invasive techniques like laparoscopy are expected to remain at the forefront of surgical advancements, offering patients safer and more efficient options for treating various medical conditions.
A Word From Hegde Fertility
Laparoscopic surgery represents a major advancement in the field of medicine, offering numerous benefits over traditional open surgery. From smaller incisions and quicker recovery times to less pain and lower complication risks, laparoscopic procedures have transformed the way surgeons treat conditions ranging from gallbladder disease to reproductive health issues. As technology continues to evolve, laparoscopy will undoubtedly remain a key player in providing patients with the highest quality care in a minimally invasive format.